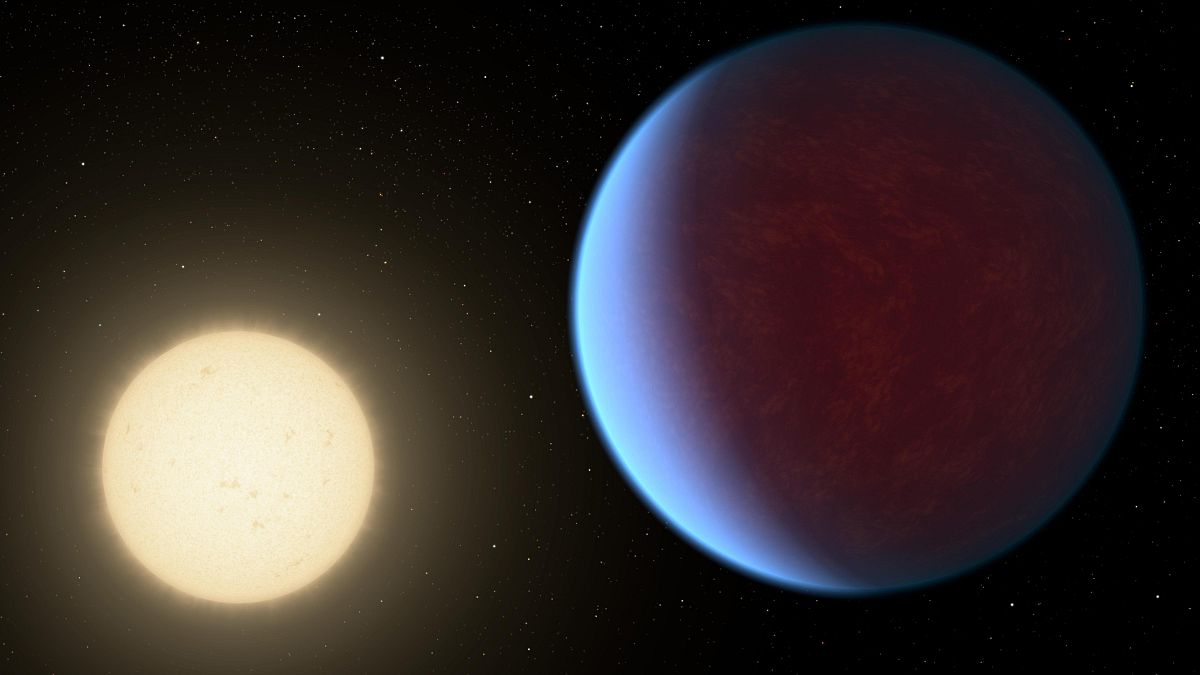
A thick atmosphere has been detected around the planet that's twice as big as Earth in a solar system about 41 light years away.
Astronomers have detected a thick atmosphere around a planet that’s twice as big as Earth in a nearby solar system, according to new research published on Wednesday.
The so-called "super Earth" - known as 55 Cancri e - is among the few rocky planets outside our solar system with a significant atmosphere, wrapped a blanket of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide.
The exact amounts are unclear. Earth’s atmosphere is a blend of nitrogen, oxygen, argon and other gases.
"It’s probably the firmest evidence yet that this planet has an atmosphere," said Ian Crossfield, an astronomer at the University of Kansas who studies exoplanets and was not involved with the research.
The research was published in the journal Nature.
"Super Earth" refers to a planet’s size, which is bigger than Earth but smaller than Neptune.
The boiling temperatures on this planet - which can reach as hot as 2,300 degrees Celsius – mean that it is unlikely to host life.
Instead, scientists say the discovery is a promising sign that other such rocky planets with thick atmospheres could exist that may be more hospitable.
Magma oceans holding atmosphere steady
The exoplanet 41 light years away is eight times heavier than Earth and circles its star Copernicus so closely that it has permanent day and night sides.
A light-year is nearly 9.7 trillion km. Its surface is encrusted with magma oceans.
To identify the makeup of its atmosphere, researchers studied James Webb Space Telescope observations before and after the planet passed behind its star.
They separated the light emitted from the planet versus its star and used the data to calculate the planet's temperature.
There's evidence the planet's heat was being distributed more evenly across its surface – a party trick atmospheres are known for.
Gases from its magma oceans may play a key role in holding its atmosphere steady. Exploring this super Earth may also yield clues to how Earth and Mars might have evolved first with magma oceans that have since cooled, scientists say.
"It’s a rare window," said Renyu Hu, a planetary scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, who was part of the research.
"We can look into this early phase of planet evolution".